Running a business online is great, but it comes with risks. Payments online? A big target for hackers. They want your customer’s credit card info. Imagine a data breach – your customers’ data stolen. Your business could lose money and trust. PCI DSS Compliance? It sounds complicated, but it’s key if you take card payments. Think of this PCI DSS Compliance Checklist as your payments security guide. In this PCI DSS Compliance Checklist we will guide you through to take all the steps before attempting for the certification.
What is PCI DSS Compliance?.
PCI DSS means Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard. It’s a long name and a simple idea. It’s a list of security rules. These rules protect credit card data. Every time someone pays with a card, PCI DSS is important. Big or small business matters to you. The PCI Security Standards Council made these rules. They’re the experts on payment security. Big card companies like Visa and Mastercard are part of it. PCI DSS is like a shield for payment data. It stops thieves and fraud. It’s not just a suggestion; it’s the rule for safe card payments.
Why Was PCI DSS Implemented?.
PCI DSS started because of too much card fraud. Online payments were becoming popular, but so were data breaches. Card companies saw a big problem: Fraud was hurting businesses and customers. So, they worked together and made PCI DSS. The point? Stop credit card theft and make online payments safer for everyone. It’s about stopping problems before they happen, not just fixing them after. PCI DSS makes payments safer for all.
What If You Are Not PCI DSS Compliant?
Ignoring PCI DSS is a bad idea. It’s really risky. First, you get fines—big fines—thousands of dollars every month if you don’t follow the rules. And then, there are data breaches. If you don’t comply with PCI DSS and get hacked, the costs go way up—fixing the breach, legal fees, and paying back customers.
Your business name suffers. People won’t trust you after a breach. Sales will drop. Your brand gets hurt. The worst thing? You might not be allowed to take card payments anymore. No cards mean less business. PCI DSS isn’t just paperwork. It’s about protecting your business, money, and reputation.
PCI DSS Levels: Which Level Is Your Business?
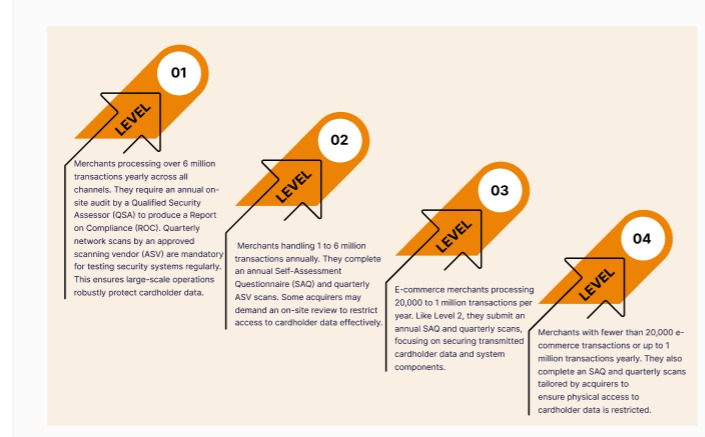
PCI DSS has four levels, based on the number of card payments you make each year. Knowing your level is important. It tells you exactly what security steps you need to take.
- Level 1: Merchants processing over 6 million transactions yearly across all channels. They require an annual on-site audit by a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) to produce a Report on Compliance (ROC). Quarterly network scans by an approved scanning vendor (ASV) are mandatory for testing security systems regularly. This ensures large-scale operations robustly protect cardholder data.
- Level 2: Merchants handling 1 to 6 million transactions annually. They complete an annual Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) and quarterly ASV scans. Some acquirers may demand an on-site review to restrict access to cardholder data effectively.
- Level 3: E-commerce merchants processing 20,000 to 1 million transactions per year. Like Level 2, they submit an annual SAQ and quarterly scans, focusing on securing transmitted cardholder data and system components.
- Level 4: Merchants with fewer than 20,000 e-commerce transactions or up to 1 million transactions yearly. They also complete an SAQ and quarterly scans tailored by acquirers to ensure physical access to cardholder data is restricted.
PCI DSS Compliance Checklist
Install and Maintain Firewall Configurations
Firewalls are your frontline defense as network security solution, shielding cardholder data from external threats. Install and maintain firewalls at every internet entry point and between internal networks and public zones. Configure them to block unauthorized traffic, allowing only essential services. Regularly review and update rules every six months to adapt to new vulnerabilities. Document configurations and ensure they align with business needs. This step prevents breaches by securing system components, a cornerstone of PCI DSS 4.0. Partners of Defend My Business can deploy robust firewall solutions to keep your network impregnable.
Eliminate Vendor-Supplied Defaults
Vendor-supplied defaults like “admin” passwords are hacker magnets. Replace them immediately on all devices, routers, POS systems, and servers handling stored cardholder data. Disable unnecessary accounts and services to shrink your attack surface. Before deployment, audit new equipment for default settings. Document changes to prove compliance during assessments. This simple step thwarts easy exploits, ensuring your systems aren’t low-hanging fruit for attackers aiming to breach access to cardholder data.
Protect Stored Cardholder Data
If you store cardholder data, render Primary Account Numbers (PAN) unreadable using encryption (e.g., AES-256), truncation, or tokenization. Avoid storing sensitive authentication data (CVV, PIN) post-authorization unless critical, then delete it securely. Use strong key management to generate, store, and rotate keys annually. Secure backups and logs, too. This requirement slashes breach impact, protecting your business from costly leaks. Our partners offer encryption tools to lock down stored cardholder data effectively.
Encrypt Transmitted Cardholder Data
When transmitted cardholder data crosses public networks, encrypt it with robust protocols like TLS 1.3 or IPsec. Avoid weak standards (e.g., SSL 3.0) and unencrypted channels like email for PANs. Manage encryption keys securely using trusted certificates. Test connections to ensure encryption holds. This shields data in transit, a vital step in the PCI DSS Compliance , preventing interception by cybercriminals exploiting open networks.
Deploy and Update Anti-Virus Software
Install anti-virus software on all systems prone to malware – PCs, servers, and gateways. Keep it regularly updated with the latest definitions to tackle new threats. Schedule frequent scans and ensure it can’t be disabled without authorization. This protects system components handling cardholder data, reducing malware risks that could expose sensitive information. Partner solutions can automate this for seamless compliance.
Maintain Secure Systems and Applications
Patch systems and applications within 30 days of critical updates to fix vulnerabilities. Use secure coding practices (e.g., OWASP guidelines) for custom software to prevent flaws like injection attacks. Implement a change control process and test and approve updates before rollout. Regularly updating ensures your defenses evolve with threats, a key part of the PCI DSS requirements.
Restrict Access to Cardholder Data
Limit access to cardholder data on a need-to-know basis by implementing access control system. Use role-based access controls (RBAC) to assign minimal permissions. Review access quarterly, revoking unneeded rights. Add multi-factor authentication (MFA) for remote access. This implements strong access control measures, shrinking the window for insider threats or unauthorized breaches, a critical compliance pillar.
Assign Unique User IDs
Every individual accessing cardholder data needs a unique ID—no shared accounts are allowed. Pair this with strong passwords and MFA for admin or remote access, track actions to specific users for accountability, and regularly audit IDs to remove dormant ones. This step, rooted in the PCI DSS requirements, ensures traceability and strengthens security by restricting access to cardholder data.
Restrict Physical Access to Cardholder Data
Secure physical locations, servers, paper records, and backups with locks, badges, or biometrics. Log and monitor entry to sensitive areas. Shred or incinerate obsolete media. Restrict physical access to prevent theft or tampering with physical access to cardholder data. Partners can supply advanced access control systems, ensuring compliance with this often-overlooked requirement.
Monitor Network Access
Log all activity on networks and systems handling cardholder data, who accessed what, when, and how. Include timestamps, event types, and success/failure details. Secure logs against tampering and retain them for a year (three months readily available). Synchronized clocks ensure accuracy. This enables rapid breach detection, a must for the PCI DSS Compliance.
Regularly Test Security Systems
Regularly test security systems with quarterly vulnerability scans by an ASV and annual penetration tests. Scan internally, too, fixing high-risk issues promptly. Test after significant changes to catch new weaknesses. This proactive step identifies exploitable flaws, keeping your defenses tight per PCI DSS 4.0 standards.
Maintain an Information Security Policy
Craft a policy covering all PCI DSS requirements, from encryption to access controls. Train staff annually on it and update it annually or after major changes. Include an incident response plan for breaches. This ensures everyone knows how to protect cardholder data, aligning your team with compliance goals.
Conduct Frequent Vulnerability Scans
Beyond quarterly scans, run vulnerability checks after a network or app changes. Use internal and external scans to spot weaknesses in system components. Fix critical issues fast and rescan to confirm. Document everything for audits. This extra layer of regular testing fortifies your compliance stance, reducing breach risks.
Perform Penetration Testing
Annual penetration tests simulate real attacks, probing network and app layers for vulnerabilities missed by scans. They should also be conducted after significant upgrades. Use qualified testers and document findings and fixes. This rigorous testing, part of regular testing, ensures your defenses hold against sophisticated threats targeting cardholder data.




